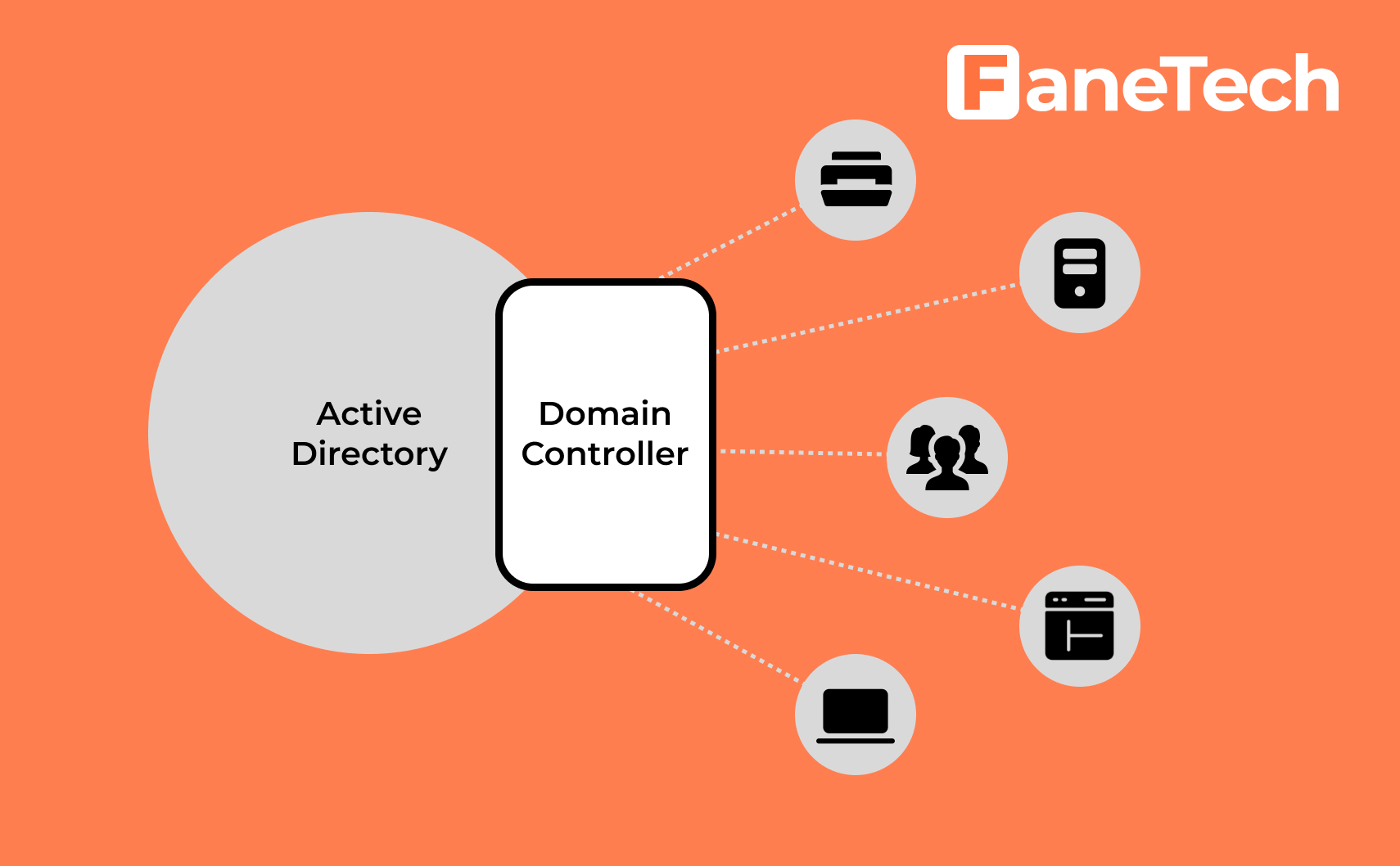
A domain controller (DC) is a type of server needed to centralize user data and protect network security. The most important function of a domain controller is to ensure that only appropriate and trustworthy users can access network resources by processing authentication requests and verifying users.
The Domain Controller allows access to domain resources and enforces security protocols, and therefore it stores user account information and runs Active Directory Domain Services (ADDS). Organizations typically have multiple domain controllers, and each one uses a copy of Active Directory.
The domain controller can be a separate system, but is often installed in clusters to improve availability and reliability. When domain controllers are running Windows Active Directory (AD), each cluster will have a primary domain controller (PDC). It must also have backup domain controllers (BDCs).
Why domain controllers are an important part of Active Directory
Domain controllers provide physical storage for the AD DS database. Moreover, they also provide services that enable businesses and IT professionals to manage their servers, computers, laptops, users, printers, and other applications. They are vital to your network and must be protected. An attacker, if they can gain control of a domain controller, could wreak havoc by destroying your AD database.
Are domain controllers and Active Directory the same thing?
A domain controller essentially contains Active Directory content. Active Directory is software that centrally stores your network in the form of a database. Domain controllers physically contain the information stored in your Active Directory.
Do I need a domain controller?
If your organization has 5 or fewer users, you can get by without an Active Directory environment. However, you will have local accounts on each of your users' computers, and you will have to maintain a list of user accounts and passwords on each computer.
Functions controller domain
The domain controller authenticates users before allowing them access to network resources. For example, a domain controller in a Windows AD domain will obtain authentication credentials from Active Directory. Let's take a closer look at its most important functions:
Examination And authentication
The domain controller first authenticates users to see if they are authorized to access the network. A user's identity is verified by verifying their account information, such as username and password, by comparing it with information stored in Active Directory.
Permission And regulation access
The domain controller manages the organizational hierarchy of users. It uses Active Directory to determine whether a user is allowed to access domain resources, and then identifies their rights to verify which resources they should have access to.
Implementation group politicians
The domain controller is responsible for implementing security protocols and rules. Some examples of these rules:
- Password update frequency requirements
- Granting access to resources to specific users
- Configure devices in a domain to enter a locked state after a specified period of inactivity
Importance controller domain
Domain controllers are responsible for controlling access to the domain and preventing unwanted access to domain networks. Because they control access to the network, they can be a prime target for a hacker trying to disrupt your network.
Here are the main reasons why a domain controller can be beneficial for an organization:
- This simplifies administrative work.
- This ensures maximum security for the corporate network.
- It centralizes control over user settings.
- This increases collaborative potential within the domain.
Restrictions controller domain
You should not rely solely on domain controllers to prevent unwanted network access. They have several limitations such as:
- Domain controllers require additional security mechanisms and infrastructure.
- Since the domain controller is responsible for authenticating users, its failure will damage the network.
- A failed domain controller can also cause network damage, making it a common target for cyberattacks.
- Networks depend on domain controllers. Therefore, to reduce the risk of downtime, it is best to deploy them in clusters.
How do controllers domain more safe
Because domain controllers are important, it is necessary to ensure their security. Here are a few steps companies should take to protect their domain controllers:
- Domain Controller Monitoring and Auditing
- Limit remote and physical access to the domain controller
- All virtual domain controllers must run on dedicated physical hosts
- Grant domain administrator access to only a few users.
- Implement strong security protocols and strict authentication processes such as multi-factor authentication
- No internet connection on the domain controller server
- Domain controllers must be running the latest version of the operating system
- Implement user activity monitoring to gain insight into all user activities on the network.

How to Configure Domain Controllers in Active Directory
Active Directory servers can handle authentication requests, but as discussed earlier, it's best not to be reliant on a single domain controller, even if you're a small company. It is recommended to have a primary domain controller and one or more backup domain controllers.
Each domain controller must be deployed on a dedicated physical server. If you have a virtual domain controller, it must run on a dedicated virtual machine running on a secure physical host.
Here are the two basic steps to configure domain controllers:
Domain assessment. Evaluate the domain where you want to configure a domain controller. Find out what type of domain controllers you need and where they will be located. Also determine their compatibility with the existing system.
Security. Domain controllers must be protected not only from external, But And from internal attacks . The data center architecture must be protected from failures such as power loss, communication loss, and system failure.
Conclusion
While the domain controller is not the only component of your network security, it certainly plays an important role. In addition to helping keep your network secure, it also
- Restricts access to sensitive data
- Stores user account information
- Ensures password security
- Blocks inactive devices
- Reduces administrative burden
Domain controllers are critical to the security of your network and, ultimately, to the success of your company. Taking the time to install and maintain a domain controller can save you a lot of problems down the road. For consultation, you can also contact our specialists at Fanetech. We are a Microsoft partner in Kazakhstan and the CIS countries.

