Power Platform is a powerful tool for business automation. In this article we will talk about Power Apps, Power Automate, and about Common Data Model and Common Data Service.
We will talk about the capabilities of the platform and the main problems encountered when automating work processes.
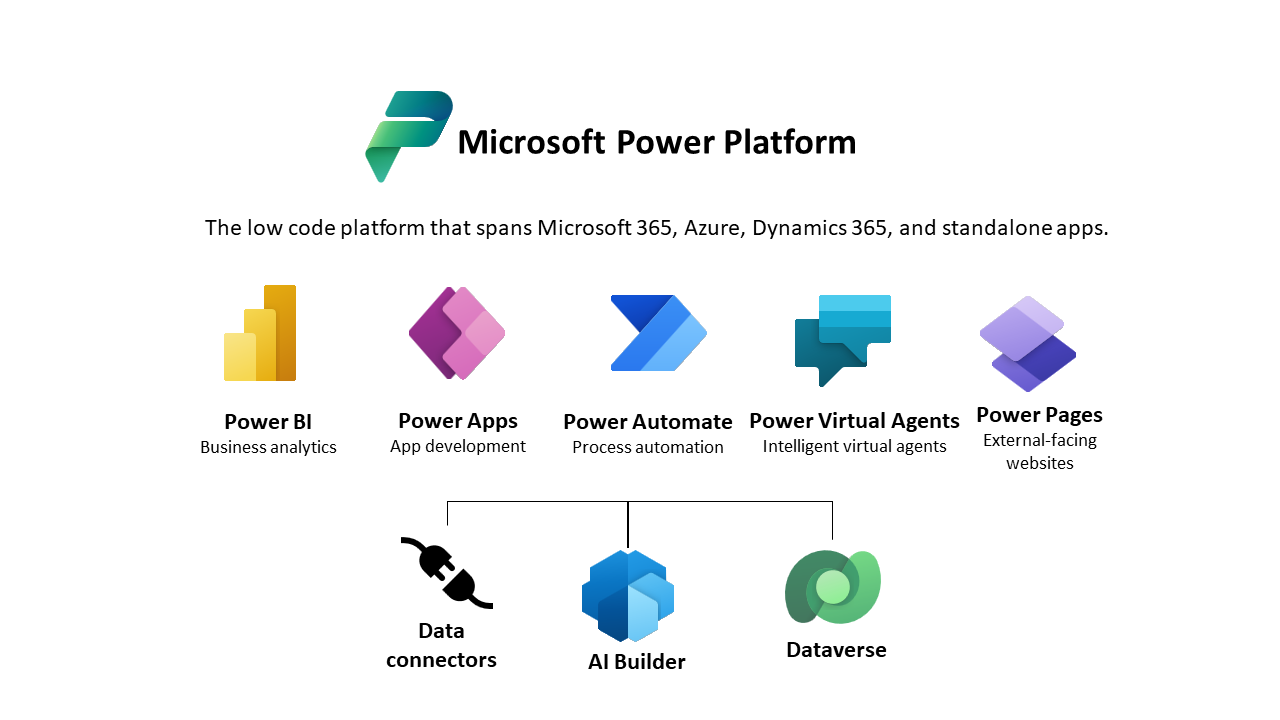
Power Platform Elements
Power BI is Microsoft's reporting and analytics platform. It's really about collating data from different sources with little or no code for more important processing. Obviously, you can choose a more significant place to process the data model, but in most cases, especially within the Power Platform, you can actually connect to your data and drag fields onto the screen to create useful reports.
Power Apps is a low-code Microsoft application builder. Essentially, it allows you to create applications that can be distributed or deployed across multiple form factors and devices in a single solution. Essentially, it is used to collect or capture data, so if you have a gap in your business process, if there is a gap in that data collection, Power Apps can be used to create an app that will run on your phone for that. on-site data collection.
Power Automate, formerly Microsoft Flow, is Microsoft's business integration platform. Using a drag-and-drop style interface and virtually no code, you can piece together an automated workflow or integrate it with various systems.
Common Data Model
The common data model is intended only to centralize the definition of your data. It is based on an open source project and is used in the Power Platform. The Common Data Service, which implements the Common Data Model, is actually the data store that you use to communicate between the three applications within the Power Platform. Here you can create a database, Power App to collect data and you can also integrate this storage with other systems.
There is a ready-made Power BI Common Data Service connector that allows you to drag and drop fields from Common Data Service to create a report. Data streams are used to receive and shape data on its way to the Shared Data Service.
Power Platform offers more than two hundred and fifty ready-made connectors.
Finally, you can share apps with others by simply sending a link in the app.
Power Apps
Power Apps is Microsoft's solution for creating low-code apps. There are different variants of Power Apps, how to license them, and how to use them.
There are Power Apps for Office 365 , and it's really about extending the capabilities of the Office 365 suite. It is designed or intended for use with Office 365. For example, if you need data collection and that data needs to be stored in a Sharepoint list or something like that, you can create a Power App to connect directly to it. This Power App can be licensed under your existing Office 365 license.
There is also Power Apps for Dynamics 365. In a similar scenario, it is designed for use with Dynamics 365. The cost of Power Apps for Dynamics 365 is included in the full user license for Dynamics 365.
Unlike Office 365, the Dynamics 365 Power Apps license includes access to the Common Data Service as well as access to on-premises data. Office 365 licensing does not include these two features - it is intended for use directly with Office 365.
Power Automate
Power Automate, formerly called Flow, is Microsoft's low-code business process integration and automation product. Flows can be built to guide users through a process.
Power Automate can be used for application integration. This is where, as a business user, you may want to piece together data between two different applications. It is not intended to replace Logic Apps, which is truly an IT professional's tool. In contrast, Power Automate is accessible to the business user.
There are pre-built connectors that can be used with Power Automate in a similar way to Power Apps. If these connectors are not suitable, you can create your own connectors, and for everything else there is a Rest API connector. Essentially, it allows you to connect to almost any Rest endpoint. From an integration point of view, the possibilities are quite wide.
Intelligent Automation
There is an update to a component from Power Automate called UI Flows, and it is a robotic process automation tool from Microsoft.
Robotic automation allows you to replay or record what a user typically does. This feature should really be used where a developer cannot be involved, or there is no API, or there is not the right level of integration to be able to connect systems. This is where Robotic Process Automation would be very useful and should be implemented in these scenarios. AI Builder can be used as part of this in UI Flows.
Conclusion
Power Platform is a comprehensive and sophisticated tool that allows you to increase the efficiency of employees and the business as a whole. If you want to deploy Power Platform in your organization, Contact us. At Fanetech, we customize Microsoft solutions and help customers get the most out of them.

